Root Diseases Caused By Basidiomycetes
Annosus Root Rot - Heterobasidion irregulare

Dried fruiting bodies of Heterobasidion irregulare.

Fruiting bodies as they appear at the base of a red pine.

The bottom pore surface of a fruiting body showing irregular shaped pores and a sterile zone with no pores at the edges.
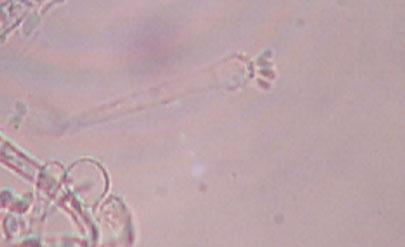
Asexual spores. The asexual form has been named Spiniger (old name Oedocephalum).
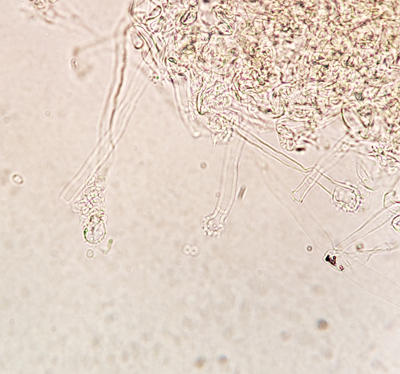
Another view of the conidiophores with spores detached.

A cross section from the base of a red pine with Heterobasidion root rot. Tree defenses, dark red resin, can be seen at the border between infected and sound wood.
Laminated Root Rot - Phellinus weirii and Phellinus sulphurascens

Fruiting bodies of Phellinus weirii.

Infected stumps and wood with this fungus have brown mycelium that contains setae. These reddish brown hair-like projections are useful to diagnose the root rot.
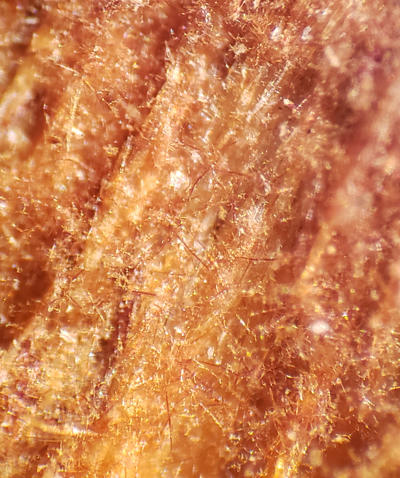

Brown setae on surface of decayed wood viewed with a hand lens. Often referred to by foresters as red whiskers

Delamination of the decayed wood often occurs at the annual rings causing the growth rings to separate. This characteristic give this root rot its common name - laminated root rot.

The decay is a white pocket rot.

Young Douglas-fir trees with Phellinus root rot.
Stand Opening Disease of Spruce - Onnia tomentosa

Decay in the roots at the lower trunk.

White pocket rot caused by Onnia tomentosa

Fruiting bodies of Onnia tomentosa.
Brown Root and Butt Rot of Conifers - Phaeolus schweinitzii
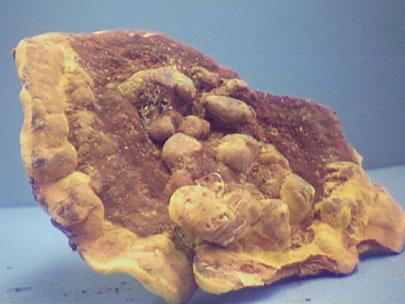
Fruiting bodies of Phaeolus schweinitzii.

The top of the fruiting bodies have a velvety appearance.

Fruiting body coming up from a decayed root.

The bottom of a fruiting body showing the pores.

Phaeolus schweinitzii causes a brown root and butt rot. Fruiting bodies can be seen in this photo on the surface of an infected stump. The brown rotted wood is also apparent.