Leaf Rusts of Hardwoods and Needle Rusts of Conifers
Poplar Leaf Rust -Melampsora medusa
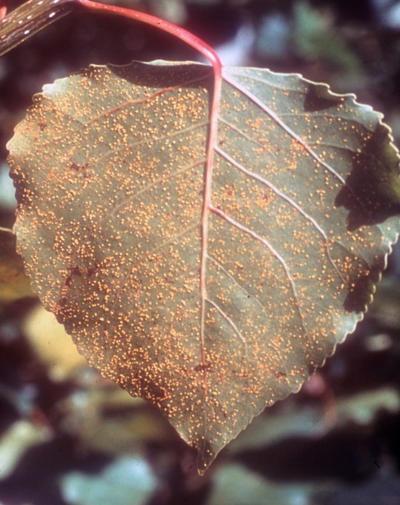

Uredinia on the bottom of a poplar leaf. They appear as small yellow fruiting bodies called sori. These produce urediniospores that reinfect poplars

Uredinia sori on leaf viewed with a hand lens.

View of the uredinia using a stereoscope.

Later in the season, telia (black spots) form on the bottom of leaf at sites where the uredinia were located.
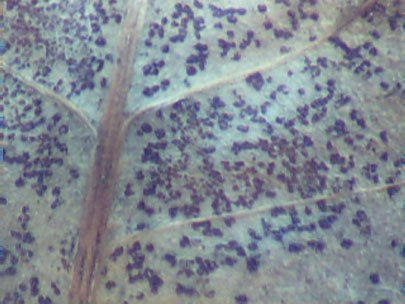
Telia appear as hardened dark fruiting bodies. The teliospores are embedded in the telium which is in the leaf.
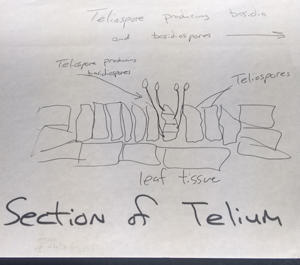
Diagram showing teliospores in the leaf and basidiospores being produced. The basidiospores infect larch.

Two leaves as seen under the sterioscope. A leaf with uredinia is on the right and a leaf with telia is on the left.

Pycnia and aecia of poplar leaf rust are produced on larch and fir needles. Aecia can be seen in this photo.

Another related rust is willow rust, caused by a different Melampsora species. Aecia can be seen on these leaves.
Red Pine Needle Rust -Coleosporium asterum

Red pine needle rust in early spring with pycnia on the needles.

In summer aecia form on the needles producing aeciospores that infect aster and goldenrod.

Aeciospores are enclosed in a structure called a peridium (white membrane) that bursts releasing the aeciospores.

Uredinia (gold/yellow areas) on the bottom of aster leaves. Some telia are also starting to form on the leaves (dark areas).

Uredinia on the bottom of a goldenrod leaf.

Uredinia (bottom leaf in photo) and telia (top leaf in photo) on golden rod leaves in the laboratory. Another alternate host is aster.