Canker Diseases - Hardwoods
Cankers caused by Neonectria:
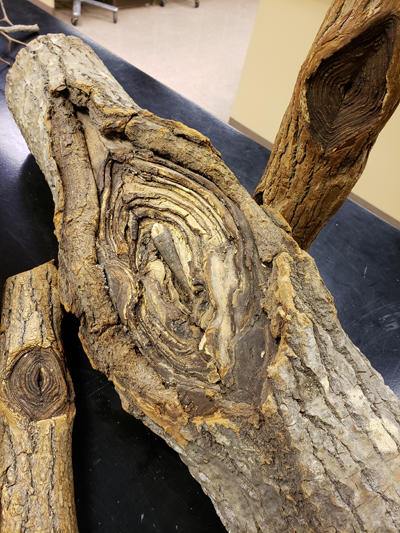

Cankers caused by Neonectria ditissima. Old name for the same fungus is Neonectria galligena (and an older name is Nectria galligena)
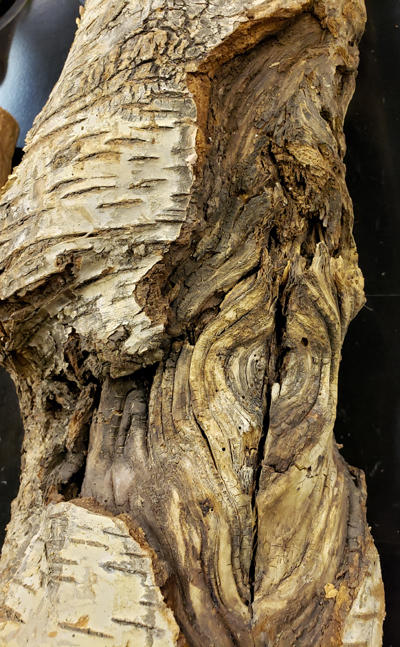

Neonectria ditissima on birch
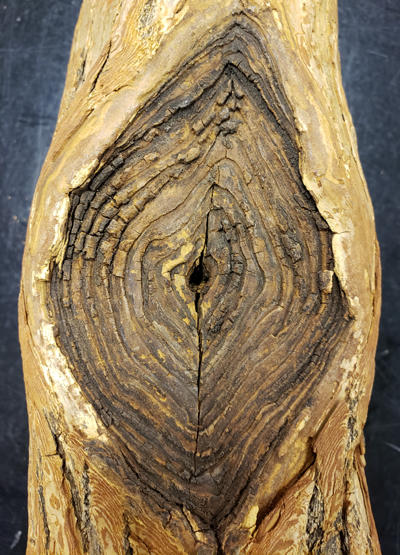

A classic target-shaped Neonectria canker on sassafras. Note old branch stub in the center where the canker started. The fungus entered a wound on this small branch and moved down the branch and into the main stem.
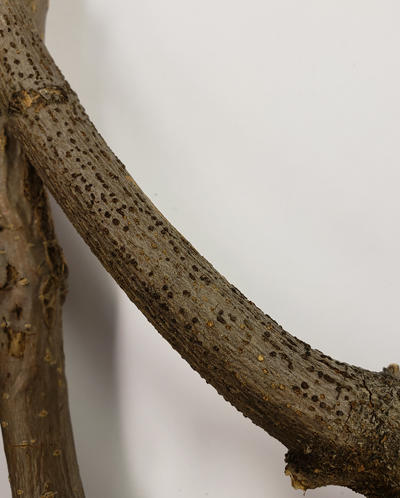

Cankers on branches produce sporodochia soon after infection. Here a small branch was killed by the fungus and sporodochia (black when dry but can be reddish colored when fresh) formed producing asexual spores.

Neonectria canker with perithecia (small reddish structures - a little hard to see) formed on some of the bark adhering to the canker face.

Red perithecia of Neonectria formed on the edge of a canker. The perithecia produce ascospores that cause new infections.
Nectria Cankers on Honey Locust:
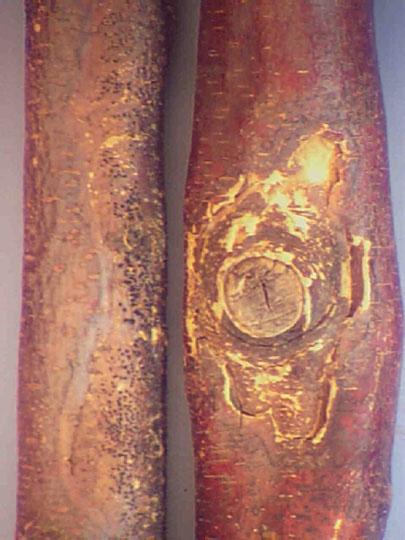

Nectria cinnabarina on a thornless and seedless cultivar of honey locust.
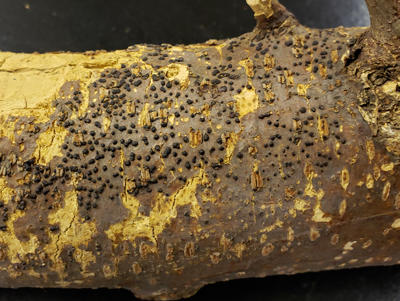
Sporodochia producing asexual sores are produced on the cankers.
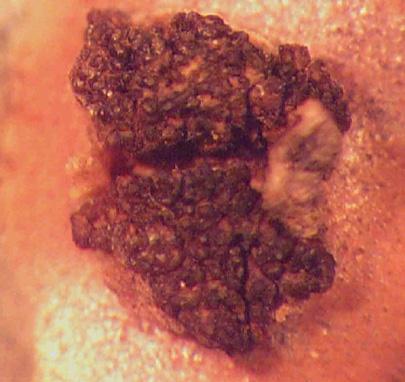
Nectria cinnabarina sporodochium. This cushion-shaped asexual fruiting body swells when wet and produces asexual spores.

Perithecia of Nectria cinnabarina clustered on old sporodochia.
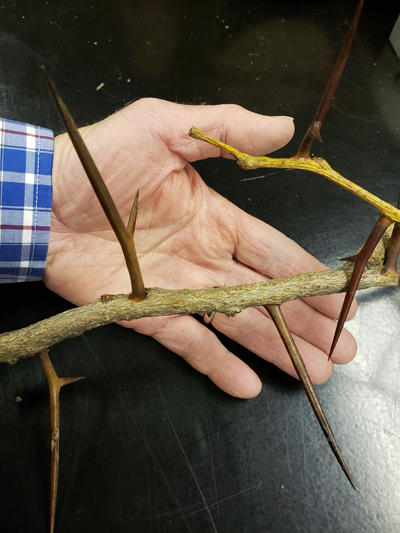


The wild type honey locust has large thorns and lots of seed pods. Cultivars selected that are thornless and seedless are very susceptible to cankers caused by Nectria cinnabarina. This fungus is usually a saprophyte on woody plants but is a serious pathogen on the thornless and seedless cultivars of honey locust.