Needle Disease
Rhabdocline pseudotsugae - on Douglas-fir

Lesions on needles caused by Rhabdocline
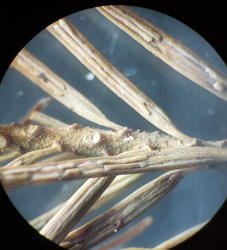
Apothecia on needles as they appear when dry.
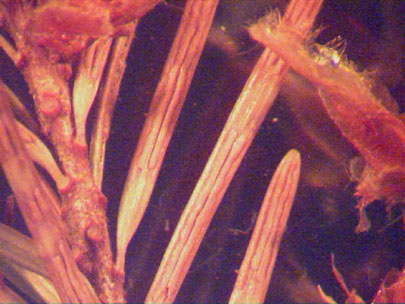
Another slightly higher magnification of apothecia when dry.

Apothecia swell up and epidermis lifts when wet and asci will release ascospores.

Another view of the mature apothecia of Rhabdocline on needles with the apothecia swelling when moisture is present. The ascospores are released in spring causing new infections.
_______________________________________________________________
Phaeocryptopus gaeumannii - Swiss Needle Cast on Douglas-fir

Infected branch from the field

Dried Douglas-fir needles with Swiss needle cast. Perithecia (numerous small black dots) can often be seen even without a hand lens if needles are inspected closely.
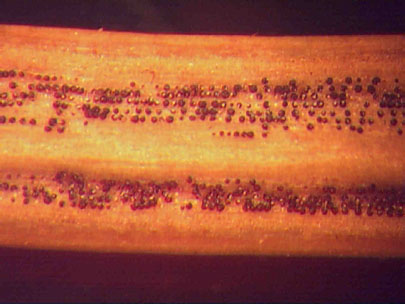
Perithecia emerging from stomata on infected needles are easily seen with a hand lens.
Didymascella thujina - on Western Red Cedar

Needle lesions containing dark round apothecia.

Higher magnification of Didymascella and apothecia
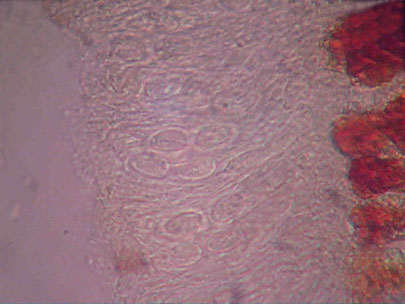
Apothecia on lesions of western red cedar produce asci with 2 ascospores per ascus.