Leaf Diseases of Hardwoods
Taphrina

Oak leaf blister caused by Taphrina.
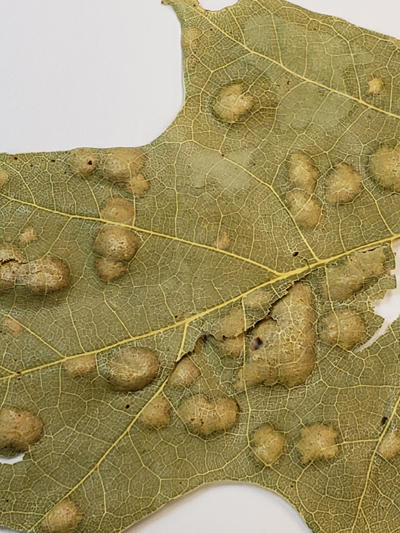

Higher magnification of an oak leaf showing the "blisters" caused by Taphrina.
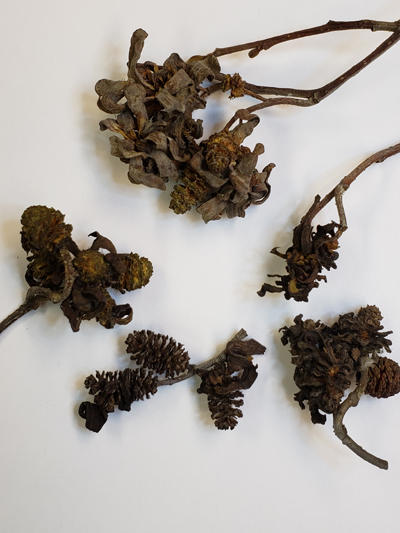

A species of Taphrina causes abnormal growths on alder.

Large growths from Taphrina on alder.

Plum pocket is caused by a Taphrina that colonizes the flower and developing fruit causing it to be deformed and distorted.
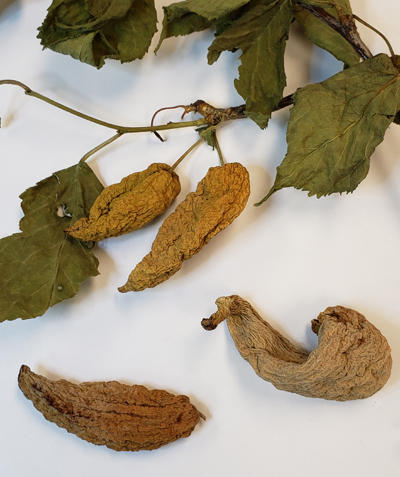

Another view of the distorted growth produced by Taphrina on plum trees.
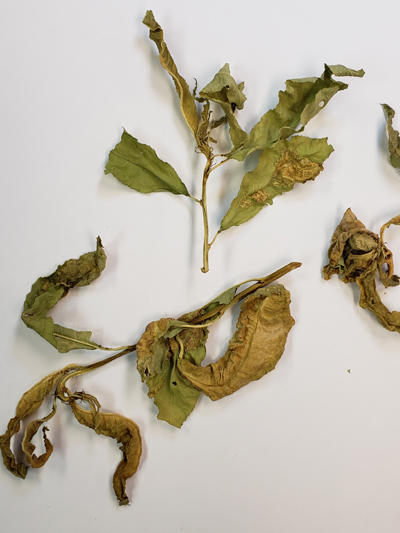

Peach leaf curl on peach caused by Taphrina.

Blisters on leaves of peach caused by Taphrina are examples of hypertropy and hyperplasia occurring in the infected leaves.
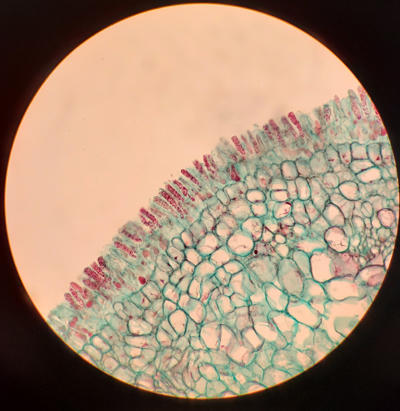
A section of an infected leaf surface showing the naked asci produced by Taphrina.
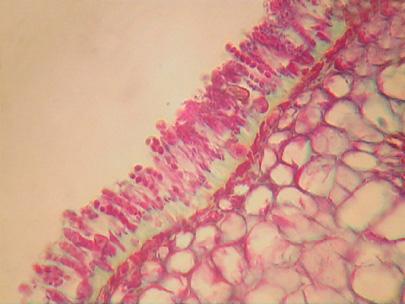
Higher magnification showing the asci produced by Taphrina on the surface of an infected peach leaf. There are 8 ascospores in each ascus but the ascospores can bud and divide producing many spores. No fruiting body or ascocarp is produced by this fungus.