Rusts
White Pine Blister Rust - Symptoms and Signs on White Pine
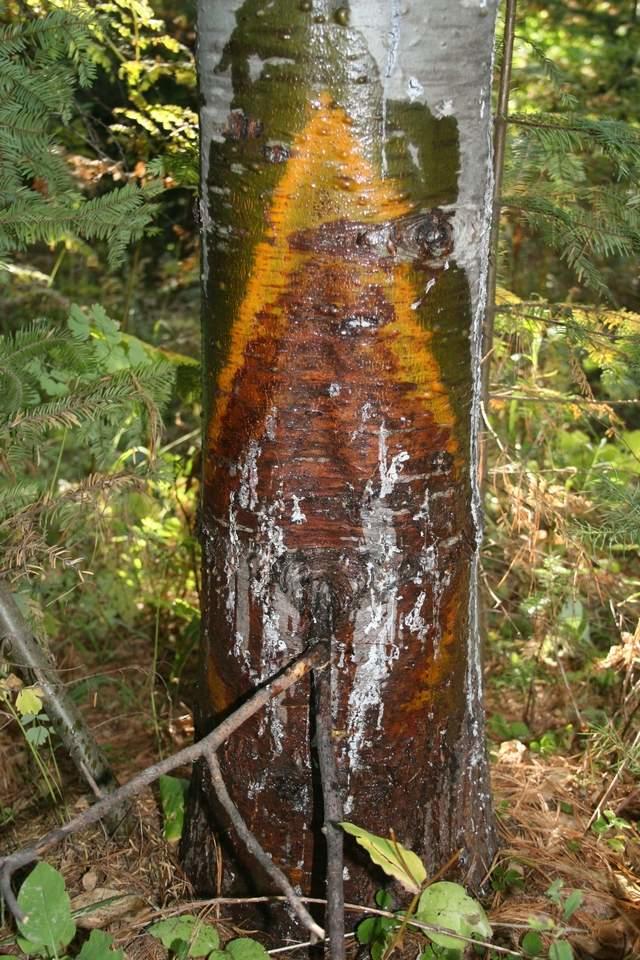

A blister rust canker in the field showing the canker lesion and resin exuding from the infected stem. Note the branch at the center where the infection entered the main stem.

Canker on the main stem of white pine with resin oozing out.
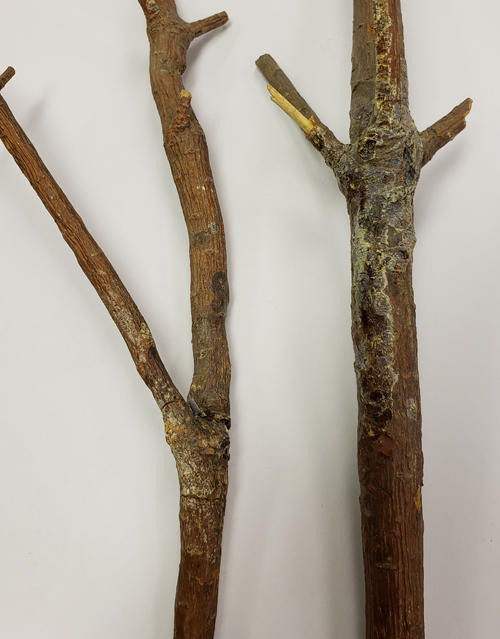

Young blister rust cankers. Pycnia would be produced on these cankers in the spring.
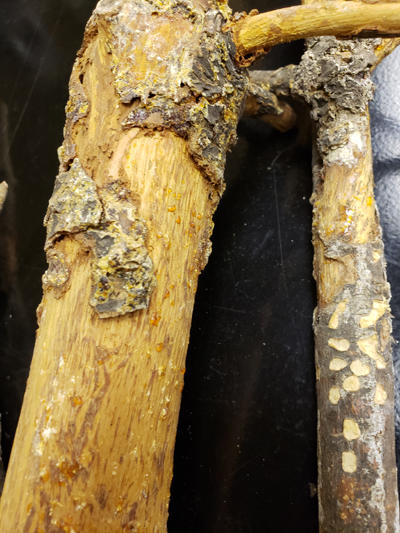

Areas on the cankers that produce pycnia are often chewed by squirrels and rodents. They are attracted to the sweet pycnial fluid that oozes out of the pycnia.

Aecia on canker of white pine.

The blister-like aecia have a white peridiurm that ruptures to release the aeciospores.
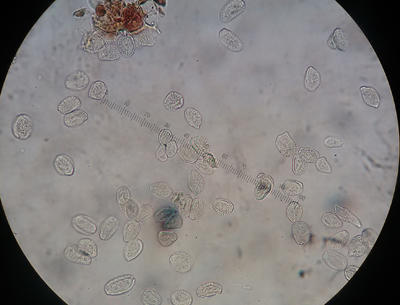
Aeciospores viewed with a microscope. Aeciospores have rough warty projections.
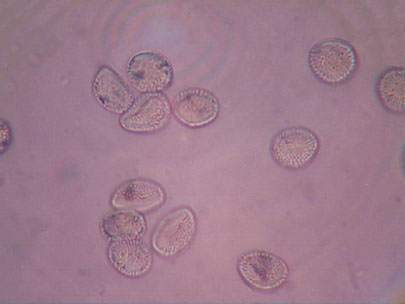
Another microscopic view of aeciospores. Note rounded projections on spores.
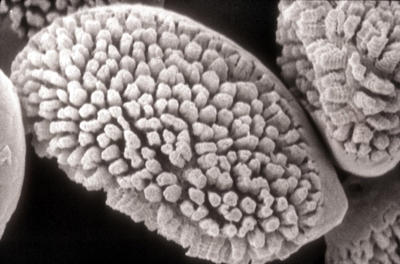
A scanning electron micrograph showing the warty appearance (rounded projections on the spore) of an aeciospore
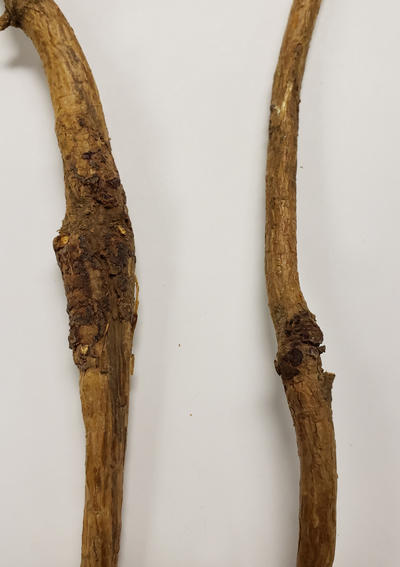

Purple mold, Tuberculina, attacking the rust fungus on two branch cankers.